10 Key Roles Responsible for Protecting CUI Compliance
Discover the key roles and responsibilities for protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).

Overview
This article delves into the pivotal roles tasked with safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) compliance within organizations. It highlights the necessity of a collaborative approach among key stakeholders—company leadership, CUI program managers, IT teams, and subcontractors—to ensure adherence to regulatory standards and effectively mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Why is collaboration critical? Engaging multiple parties fosters a comprehensive understanding of compliance requirements and promotes a culture of accountability. Each stakeholder must recognize their responsibilities in maintaining CUI integrity, which is essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
Furthermore, organizations must implement robust training programs and resources that empower these stakeholders to fulfill their roles effectively. By doing so, they not only enhance compliance but also build a resilient framework against potential data breaches.
In conclusion, a unified effort is paramount in achieving CUI compliance. Organizations should take proactive steps to engage all relevant parties, ensuring that everyone is equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to protect sensitive information.
Introduction
The protection of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) has emerged as a critical concern for organizations navigating the complexities of compliance, particularly given the increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies. It is essential for any entity aiming to fortify its data security and adhere to the rigorous standards established by the Department of Defense to understand the key roles involved in safeguarding CUI. Yet, with a myriad of responsibilities and potential pitfalls, how can organizations ensure that every individual plays their part effectively in this vital mission?
This article explores ten pivotal roles responsible for CUI compliance, providing insights into best practices and strategies that can empower organizations to cultivate a robust culture of adherence and protection against evolving cyber threats.
CMMC Info Hub: Your Guide to CUI Protection Responsibilities
CMMC Info Hub serves as an essential resource for entities who are responsible for protecting CUI. It provides structured guidance on regulatory responsibilities, empowering businesses to understand who is responsible for protecting CUI and their roles in safeguarding sensitive data. By leveraging the insights offered by the Hub, organizations can adeptly navigate the complexities surrounding who is responsible for protecting CUI, ensuring their practices align with the rigorous requirements established by the Department of Defense.
Recent developments underscore the vital significance of adhering to CUI regulations. The FAR CUI Rule mandates that all contractors, including subcontractors, adhere to new safeguarding standards, clarifying who is responsible for protecting CUI and emphasizing the need for a robust culture of compliance. This culture not only fortifies data security but also reduces risks associated with non-compliance, which can result in substantial legal consequences, particularly given the Department of Justice's heightened enforcement of cybersecurity regulations.
Current best practices for protecting CUI, which detail who is responsible for protecting CUI, involve the implementation of the NIST SP 800-171 framework that delineates the essential security controls. Moreover, contractors must ensure prompt reporting of any cybersecurity incidents, adhering to a strict 72-hour notification requirement. Engaging in proactive compliance strategies—such as conducting regular assessments and formulating Plans of Action & Milestones (POA&Ms) for identified gaps—is crucial for maintaining regulatory standards and bolstering overall security posture.
By fostering a culture of adherence and utilizing the resources available through CMMC Info Hub, entities can not only fulfill regulatory obligations but also strengthen their defenses against the escalating tide of cyber threats, including the unprecedented ransomware incidents highlighted in recent analyses.
Company Leadership: Setting the Compliance Culture for CUI Protection
Company leadership plays a crucial role in establishing a robust culture that clarifies who is responsible for protecting CUI. By actively promoting the concept of who is responsible for protecting CUI, leaders can instill a sense of accountability throughout the organization. This responsibility involves:
- Identifying who is responsible for protecting CUI
- Allocating adequate resources for comprehensive training programs
- Formulating clear policies
- Fostering open communication regarding adherence expectations
A strong adherence culture not only enhances CUI security but also fosters trust among stakeholders who are responsible for protecting CUI. Did you know that entities with reporting hotlines identify fraud via tips 47.3% of the time? This statistic underscores the critical role of leadership in developing effective reporting systems. Furthermore, an impressive 84% of entities provide reports on adherence status, which emphasizes who is responsible for protecting CUI and the strategic significance of prioritizing its safeguarding. By establishing a distinct tone from the top, leaders can effectively shape their organization's strategy concerning regulations, ensuring that the individuals who are responsible for protecting CUI are woven into the core operational framework.
CUI Program Manager: The Key Role in Compliance Oversight
The role of the CUI Program Manager is critical in ensuring regulatory oversight. This individual, who is responsible for protecting CUI, is tasked with developing and implementing policies that safeguard Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), conducting thorough risk assessments, and ensuring that all employees are aware of their responsibilities.
To achieve compliance with the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) efficiently, it is vital to adopt practical strategies such as:
- Regular policy evaluations
- Maintaining version control
- Effectively communicating changes to all staff
By coordinating adherence efforts across various departments, the CUI Program Manager establishes a robust framework for protecting sensitive information, clearly defining who is responsible for protecting CUI, transforming confusion into clarity, and instilling confidence in meeting CMMC standards.
IT and Security Teams: Implementing Technical Safeguards for CUI
IT and security teams stand at the forefront of implementing technical safeguards for Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Their responsibilities encompass deploying encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems designed to detect and respond to potential threats. To manage these crucial duties effectively, teams should consult a comprehensive System Security Plan (SSP) outline. This outline includes essential elements such as:
- System description
- Assessment scope
- Security control implementation
- Verification of adherence by external service providers
By collaborating closely with other departments, these teams ensure that technical measures are in alignment with organizational policies and regulatory requirements. This collaboration is vital in creating a secure environment for handling sensitive information.
Have you considered how these measures can enhance your organization’s security posture? By leveraging a detailed SSP and fostering interdepartmental cooperation, your organization can significantly mitigate risks associated with CUI. The proactive approach of IT and security teams not only safeguards sensitive data but also promotes a culture of compliance and security awareness throughout the organization. It is imperative to recognize who is responsible for protecting CUI, as this responsibility does not rest solely on IT; it is a collective effort that requires the engagement of all departments.
In conclusion, the integration of technical safeguards, guided by a well-structured SSP and collaborative efforts, is essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information. Organizations must prioritize these practices to ensure they meet compliance requirements and protect against evolving threats.
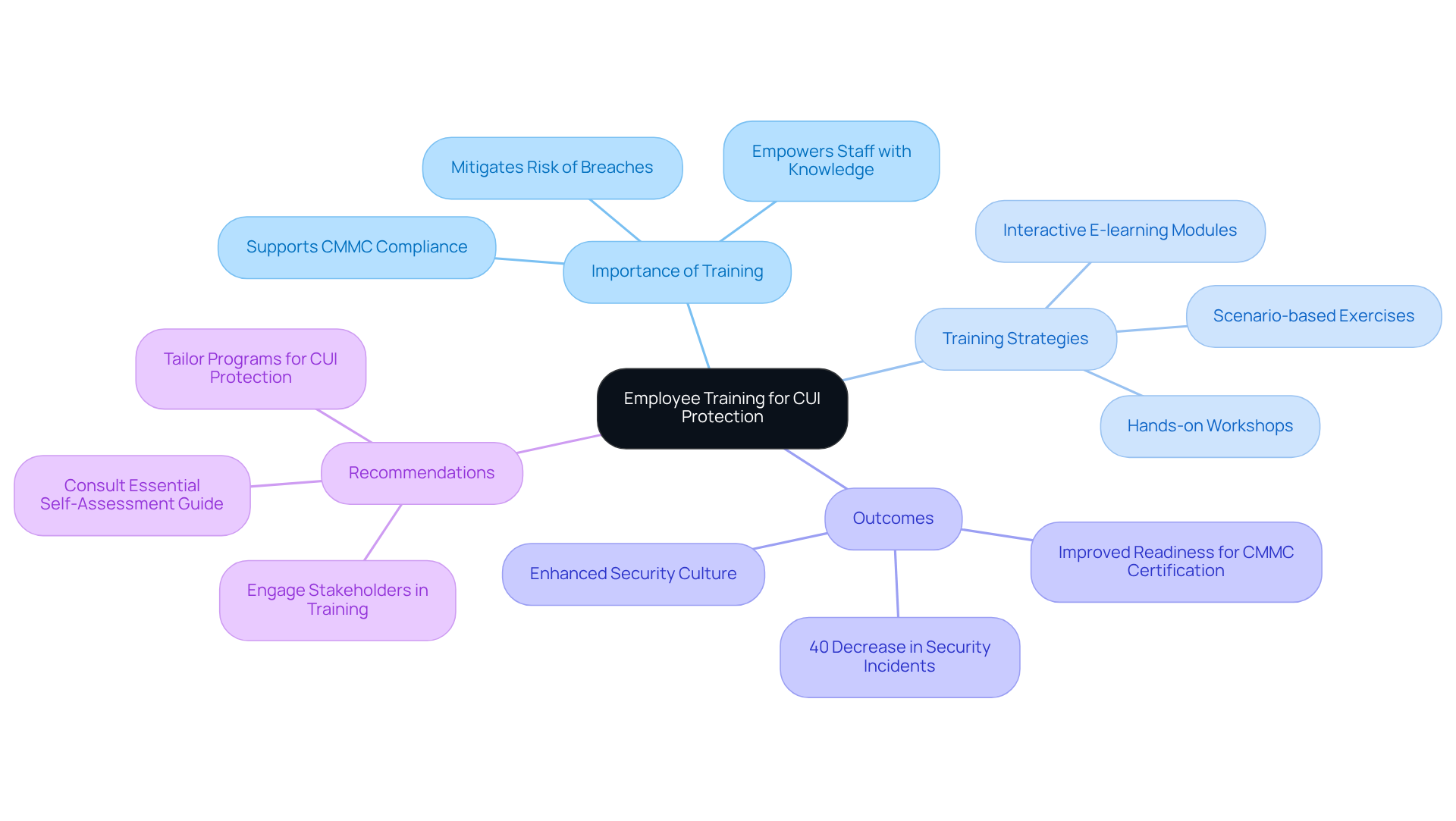
Employee Training: Empowering Staff to Protect CUI
Employee training is essential for safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and is vital for those who are responsible for protecting CUI in the pursuit of CMMC adherence. Regular training sessions must be instituted to address regulatory requirements, data handling procedures, and security best practices. These initiatives not only empower staff with vital knowledge but also significantly mitigate the risk of accidental breaches. For example, organizations that prioritize training have experienced a marked reduction in data breaches, underscoring the impact of a well-informed workforce.
Effective training strategies encompass:
- Hands-on workshops
- Interactive e-learning modules
- Scenario-based exercises that immerse employees in practical applications of security protocols
Such methodologies foster a culture of security awareness, ensuring that all team members understand their responsibilities in protecting sensitive information, particularly in light of the safeguarding requirements stipulated in FAR 52.204-21 for CMMC Level 1 adherence.
Moreover, entities that have successfully integrated comprehensive training programs into their regulatory frameworks have noted quantifiable results. A defense contractor that adopted a robust training initiative, for instance, reported a 40% decrease in security incidents over the course of a year. This illustrates the vital connection between employee education and an enhanced cybersecurity posture, in alignment with the roadmap for DoD cybersecurity success.
To bolster adherence initiatives, organizations should consider tailoring training programs specifically for those who are responsible for protecting CUI. This entails addressing the unique challenges associated with handling sensitive information and ensuring that all employees are prepared to identify and respond to potential threats. By investing in effective training programs, entities not only fulfill regulatory standards but also promote a proactive cybersecurity approach, ultimately improving their readiness for CMMC certification. Additionally, consulting the 'Essential Self-Assessment Guide for CMMC Compliance' can provide further guidance on the necessary steps for achieving adherence. As Perry Keating, Managing Director and President of Protiviti Government Services, states, 'Preparing for CMMC adherence is a strategic necessity that requires detailed planning and execution.
Legal Frameworks: Guiding Compliance for CUI Protection
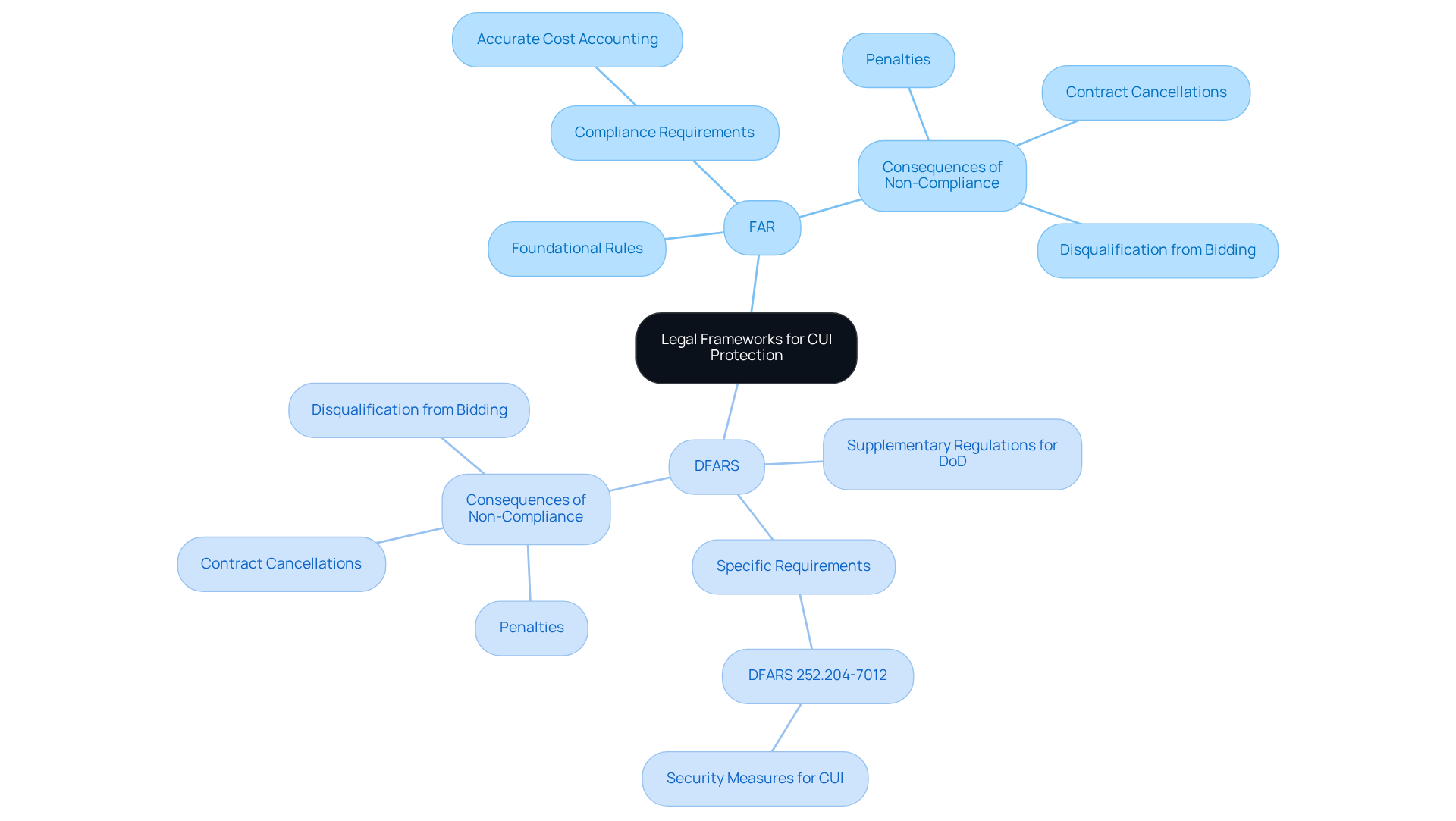
Legal frameworks play a crucial role in shaping adherence strategies for determining who is responsible for protecting CUI. Organizations must adeptly navigate the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS), which establish stringent requirements for safeguarding sensitive data. Compliance with these regulations is not merely a legal obligation; it is essential for maintaining eligibility for government contracts.
FAR outlines the foundational rules governing federal procurement, while DFARS supplements these regulations specifically for Department of Defense (DoD) contracts, emphasizing the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures. For instance, DFARS 252.204-7012 mandates that contractors implement sufficient security measures to protect CUI, clarifying who is responsible for protecting CUI and highlighting the significance of a proactive adherence stance.
Legal experts assert that non-compliance with FAR and DFARS can result in severe consequences, including penalties, canceled contracts, and disqualification from future bidding opportunities. As Joshua Lawton aptly states, "Compliance isn’t just about winning contracts—it’s about executing them successfully." This underscores the necessity for organizations to develop comprehensive policies and procedures that align with these regulations, thereby mitigating legal risks.
Recent updates to FAR and DFARS reflect a dynamic environment, with increased scrutiny on adherence practices. Organizations are encouraged to remain informed about these changes to ensure their regulatory frameworks are effective. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that this platform may contain links to external websites. We have no control over the content of these external sites and accept no responsibility for their content or availability. The inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by us. The influence of these regulations transcends simple obedience; they shape the overall culture of adherence within entities, promoting a strategic approach to risk management and data protection.
In summary, understanding the role of who is responsible for protecting CUI and implementing the requirements set forth by FAR and DFARS is vital for organizations handling CUI. By prioritizing adherence to regulations, businesses not only safeguard sensitive information but also enhance their credibility and competitiveness in the defense contracting field.
Small Manufacturers: Navigating CUI Compliance Challenges
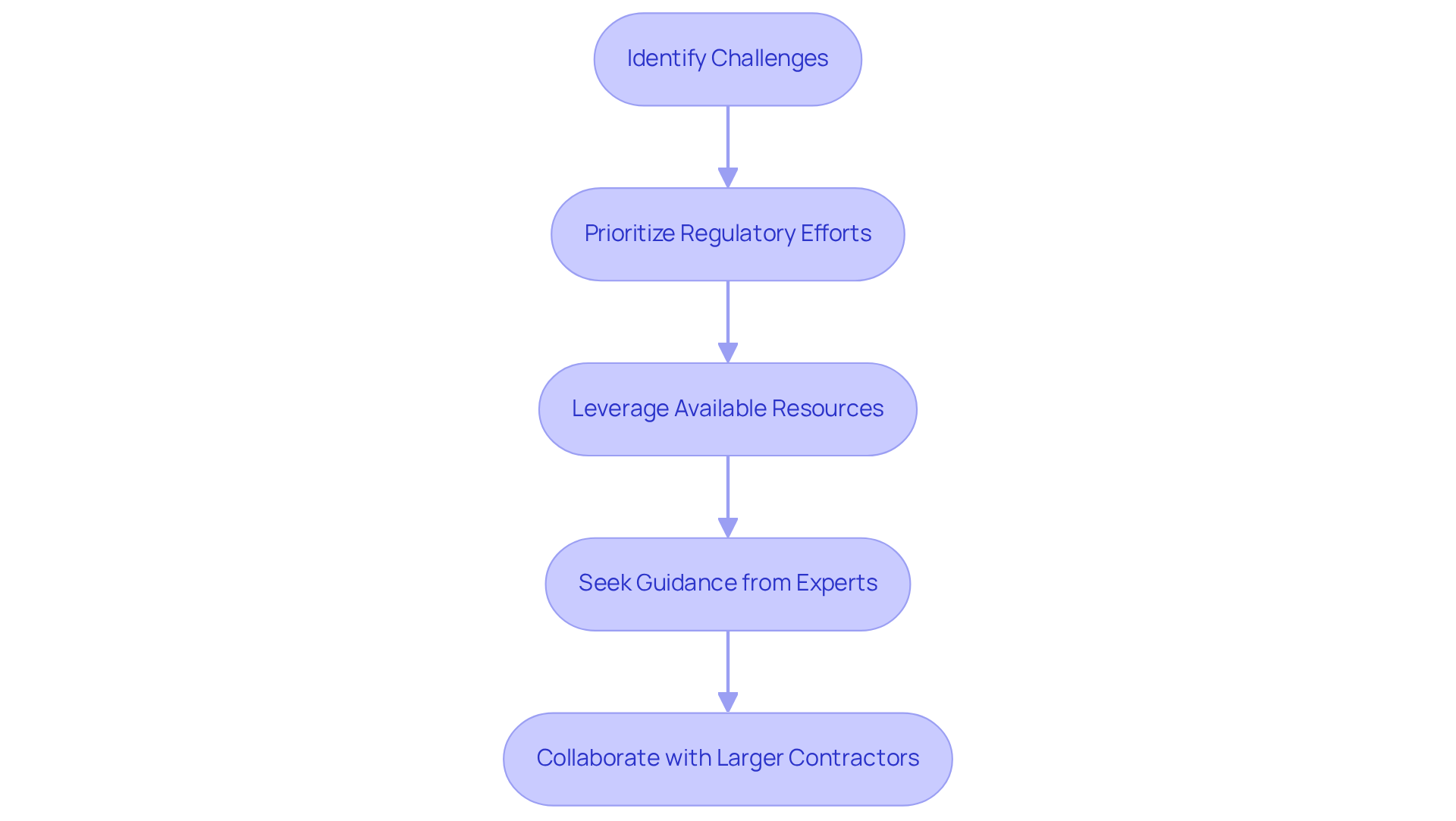
Small manufacturers often face significant challenges in complying with CUI regulations, particularly concerning who is responsible for protecting CUI, due to resource limitations and a lack of expertise. To effectively navigate these hurdles, it is crucial for them to prioritize their regulatory efforts.
By leveraging available resources and seeking guidance from industry experts, they can enhance their compliance strategies. Additionally, collaborating with larger contractors can provide valuable insights and support in meeting these regulations. This approach not only ensures compliance but also clarifies who is responsible for protecting CUI, allowing smaller manufacturers to compete effectively within the defense supply chain.
Government Agencies: Defining Standards for CUI Protection
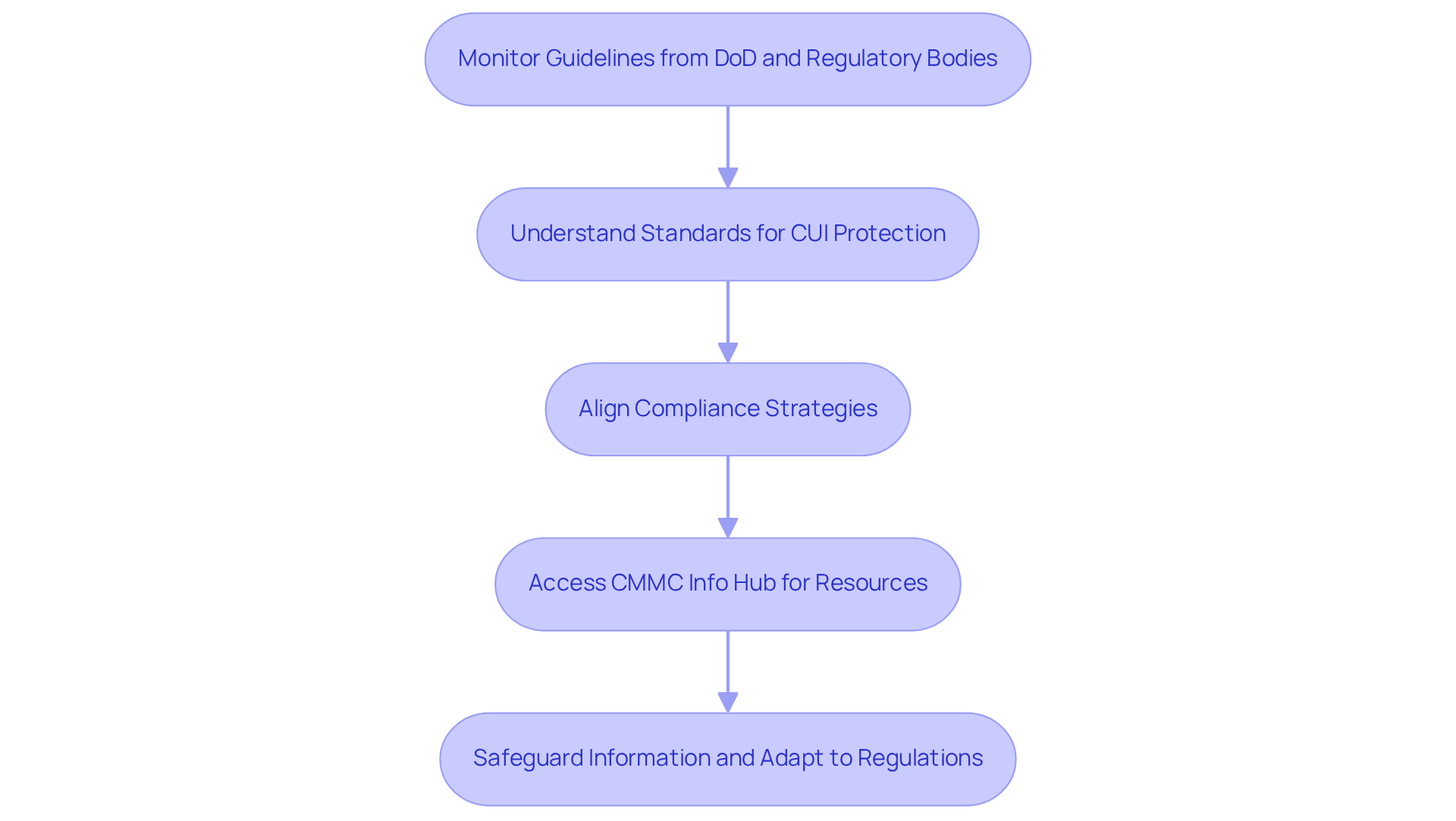
Government agencies are pivotal in determining who is responsible for protecting CUI and setting the standards for its protection. Organizations must diligently monitor the guidelines issued by the Department of Defense (DoD) and other regulatory bodies to understand who is responsible for protecting CUI and ensure compliance. By thoroughly understanding these standards, businesses can effectively align their compliance strategies with government expectations, thereby enhancing their eligibility for defense contracts.
The CMMC Info Hub serves as an indispensable resource, offering practical strategies and insights from peers that simplify the compliance process. For instance, you can access templates for regulatory documentation and case studies from entities that have successfully navigated the certification journey. This proactive approach not only safeguards sensitive information but also empowers organizations to adapt swiftly to evolving regulatory requirements, ensuring they remain competitive in the defense contracting arena.
Subcontractors: Ensuring Shared Responsibility in CUI Protection
Subcontractors are those who are responsible for protecting CUI within the defense supply chain. Effective communication between contractors and subcontractors is essential to ensure that all parties who are responsible for protecting CUI fully understand their obligations and responsibilities. By fostering a collaborative environment, organizations can establish a cohesive strategy that identifies who is responsible for protecting CUI, significantly reducing the risks associated with data breaches.
To improve adherence, contractors must implement clear communication strategies that outline specific CUI handling procedures and expectations. Frequent training sessions and updates are vital in keeping subcontractors informed of changing regulatory requirements. For instance, joint workshops can facilitate knowledge sharing and reinforce the importance of adhering to CUI protocols.
Successful examples of collaboration include:
- Joint audits
- Assessments, where contractors and subcontractors work together to identify vulnerabilities and implement corrective actions.
Such collaborations not only enhance adherence efforts but also foster trust and accountability throughout the supply chain. By prioritizing communication and teamwork, entities can effectively manage the complexities of CUI regulations and bolster their overall cybersecurity stance.
Consequences of Non-Compliance: Understanding Risks in CUI Protection
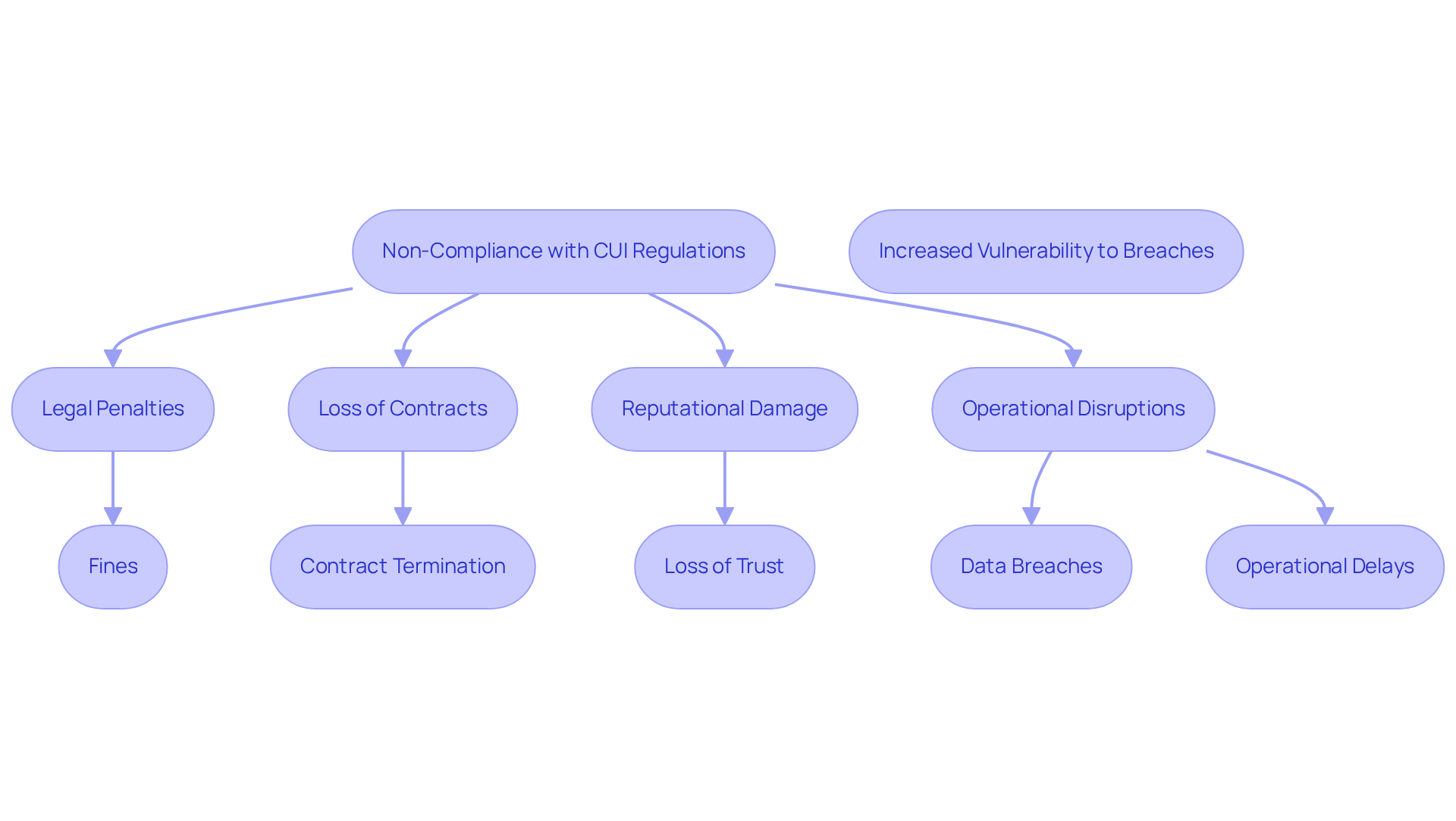
Non-compliance with Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) safeguarding regulations can lead to significant consequences for organizations. Legal penalties can be severe; non-compliant companies may face fines and potential barring from future federal contracts. A recent study revealed that over 30% of defense contractors incorrectly categorized CUI alongside classified data, which can lead to improper safeguarding and increased vulnerability to breaches. For instance, a 2022 review by the Department of Defense discovered that 18% of subcontractors were oblivious to their CUI responsibilities, emphasizing a significant shortcoming in awareness.
The risks associated with failing to protect CUI extend beyond financial penalties. Organizations may lose valuable contracts, suffer reputational damage, and face operational disruptions due to data breaches. Such breaches not only expose sensitive information but also jeopardize national security, creating a ripple effect that can impact the entire defense supply chain. The Department of Defense has emphasized that contractors must safeguard covered defense information; failure to do so can lead to contract termination.
Furthermore, the repercussions of non-compliance are not confined to primary contractors; it is also subcontractors and suppliers who are responsible for protecting CUI and bear responsibility for failures in safeguarding. This interconnected responsibility underscores the need for all entities involved in federal contracting to prioritize compliance and determine who is responsible for protecting CUI while implementing robust protection strategies. By understanding these risks, organizations can better motivate their teams to adhere to CUI regulations and enhance their cybersecurity posture.
This platform may contain links to external websites. We have no control over the content of these external sites and accept no responsibility for their content or availability. The inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by us.
Conclusion
Understanding who is responsible for protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is essential for organizations aiming to achieve compliance with stringent regulations. This article highlights the pivotal roles that various stakeholders play in safeguarding sensitive data, from company leadership to IT teams and subcontractors. Each role is intricately linked to establishing a culture of compliance, ensuring that all parties are aware of their responsibilities and equipped to protect CUI effectively.
The discussion covers key insights into the responsibilities of leadership in fostering a compliance-oriented culture, the critical oversight provided by CUI program managers, and the technical safeguards implemented by IT and security teams. Moreover, the importance of employee training and the guidance offered by legal frameworks are emphasized as vital components in navigating the complexities of CUI compliance. By prioritizing these roles and practices, organizations can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their overall security posture.
As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, the significance of a collaborative and informed approach to CUI protection cannot be overstated. Organizations are encouraged to leverage resources like the CMMC Info Hub to stay updated on compliance requirements and best practices. Embracing a proactive stance towards CUI safeguarding will not only mitigate risks but also contribute to a more secure and resilient defense supply chain. The commitment to understanding and fulfilling these responsibilities is crucial in protecting sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of national security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the CMMC Info Hub?
The CMMC Info Hub serves as a resource for entities responsible for protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), providing structured guidance on regulatory responsibilities and helping businesses understand their roles in safeguarding sensitive data.
Why is adhering to CUI regulations important?
Adhering to CUI regulations is crucial because it clarifies responsibilities for protecting CUI and emphasizes the need for a strong culture of compliance, which enhances data security and reduces risks associated with non-compliance, including legal consequences.
What are the current best practices for protecting CUI?
Current best practices include implementing the NIST SP 800-171 framework, promptly reporting cybersecurity incidents within 72 hours, conducting regular assessments, and formulating Plans of Action & Milestones (POA&Ms) for identified gaps.
How can company leadership influence CUI protection?
Company leadership can influence CUI protection by promoting accountability, allocating resources for training, formulating clear policies, and fostering open communication regarding adherence expectations.
What role does the CUI Program Manager play in compliance oversight?
The CUI Program Manager is responsible for developing and implementing policies to safeguard CUI, conducting risk assessments, and ensuring that all employees understand their responsibilities related to CUI protection.
What strategies can be adopted for efficient compliance with CMMC?
Strategies for efficient compliance with CMMC include regular policy evaluations, maintaining version control, and effectively communicating changes to all staff.
How does a strong adherence culture benefit organizations?
A strong adherence culture enhances CUI security, fosters trust among stakeholders, and improves the effectiveness of reporting systems, ultimately supporting the organization's compliance efforts.




